Piles - Everything you need to know about
Piles, also known as hemorrhoids, are swollen blood vessels in the rectum and anus that cause discomfort and bleeding. Common symptoms include pain during bowel movements, itching, and rectal bleeding. Factors such as straining during bowel movements, obesity, and pregnancy can contribute to their development. Treatment options range from lifestyle changes and topical ointments to medical procedures, depending on the severity. Maintaining a high-fiber diet, staying hydrated, and avoiding prolonged sitting can help prevent and alleviate symptoms.
Symptoms of piles
Rectal Bleeding: Bright red blood during or after bowel movements is a common symptom of piles.
Pain or Discomfort: Irritation, soreness, or pain in the anal region, especially during sitting or bowel movements.
Itching: Persistent itching or irritation around the anus.
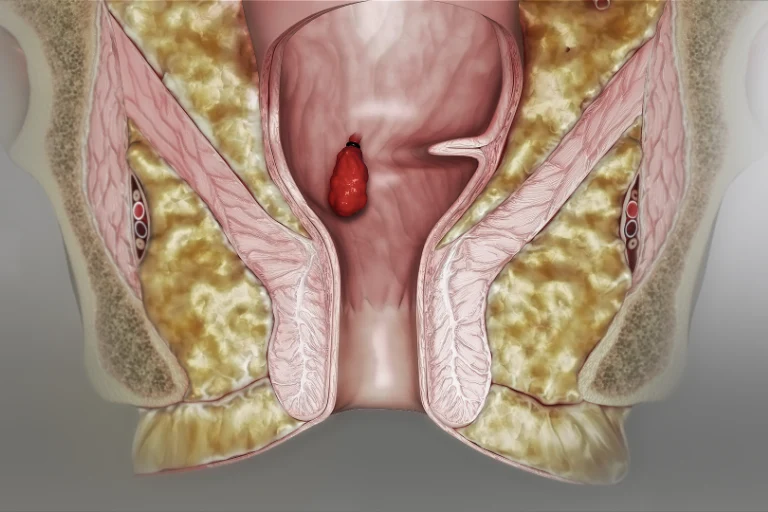
Swelling: Swollen blood vessels in the rectum and anus, causing discomfort.
Lump or Bump: A soft lump or swelling around the anal opening.
Mucous Discharge: Unusual discharge of mucous from the anus.
Incomplete Bowel Movements: Difficulty in emptying the bowels completely.
Anal Leakage: Unintentional release of feces or mucus.
Prolapse: Piles may protrude outside the anal opening during bowel movements.
Tenderness: Tenderness or sensitivity in the anal region, particularly when touched or during bowel movements.
Causes of Piles
Chronic Constipation or Diarrhea: Irregular bowel habits can contribute to the formation of hemorrhoids.
Obesity: Being overweight or obese puts increased pressure on the rectal veins, increasing the risk of piles.
Pregnancy: The pressure exerted on the pelvic veins during pregnancy can lead to the development of piles.
Aging: The aging process can weaken the tissues supporting the veins in the rectum, making them more susceptible to swelling.
Genetic Factors: A family history of hemorrhoids may increase the likelihood of developing piles.
Sitting for Prolonged Periods: Sedentary lifestyles or extended periods of sitting can contribute to hemorrhoid development.
Low-Fiber Diet: Inadequate fiber intake can lead to constipation, straining during bowel movements, and the formation of piles.
Surgical Piles Treatment
Hemorrhoidectomy: The surgical removal of hemorrhoids, particularly recommended for severe cases or when other treatments have not been effective.
- Internal hemorrhoid stapling: It is also known as stapled hemorrhoidopexy or procedure for prolapse and hemorrhoids (PPH), is a surgical procedure used to treat internal hemorrhoids. The technique involves the use of a circular stapling device to remove excess tissue and reposition the hemorrhoidal tissue back into its normal position within the anal canal. The staples are placed above the sensitive nerve endings, reducing pain compared to traditional hemorrhoidectomy.







