Laparoscopic Surgery
Dr Subash K G is one of the best Hernia Specialists practising in Bengaluru. He treats all types of hernias from simple to highly complex.
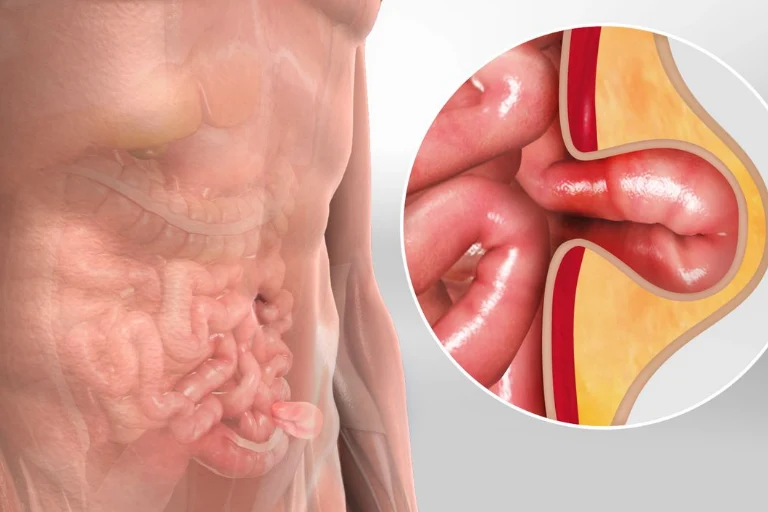
Hernias manifest as protrusions in the abdominal area, where intestines and abdominal fat emerge beneath the skin through weakened spots or openings in the abdomen. These weak points can arise from scars of prior surgeries or naturally occurring gaps in the abdominal wall, commonly found in the groin, navel, abdomen, or at the site of previous operations. As hernias are increasingly prevalent, many individuals opt for hernia surgery to effectively address this condition. It’s crucial to note that hernias don’t improve over time and won’t resolve on their own.
Symptoms of Hernia
- Lump in the groin area when standing/straining & disappears when reclining
- Pain at the site of the lump, especially when lifting a heavy object
- Swelling of the scrotum
- Excruciating abdominal pain (if you have strangulation)
- Nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite & pain (if intestinal obstruction occurs)
Hernia Treatment Procedure Types
Observation Period: If the hernia is small and asymptomatic, a watchful waiting approach may be recommended. This involves regular monitoring for any changes, such as size increase or symptom development. Lifestyle adjustments, like avoiding heavy lifting, may be suggested to mitigate the risk of hernia progression. Watchful waiting is commonly advised for inguinal hernias in men and umbilical hernias in infants.
Surgical Intervention: When the hernia is sizable or causing symptoms, surgical repair becomes necessary. Various surgical methods are available:
Open Surgery: An incision is made in the affected area to access and repair the hernia. Typically performed under general anesthesia.
Laparoscopic Surgery: Multiple small abdominal incisions are made, and a laparoscope is utilized for hernia repair. Generally performed under general anesthesia.
Robotic Surgery: A robotic system assists in hernia repair, often conducted under general anesthesia.
Support Measures: In certain cases, a truss or belt might be recommended to provide support and alleviate symptoms, particularly for small, asymptomatic hernias.
Diagnosis of Hernia
Hernia, a prevalent medical condition, occurs when an organ or tissue protrudes through a weakened area in the surrounding muscles and connective tissue. Manifesting in various body parts such as the abdomen, groin, and upper thigh, hernias necessitate thorough diagnosis. Dr. Bhushan Chittawadagi discusses the diagnostic techniques employed in identifying hernias.
Medical Examination: Initiating the diagnostic process, a medical examination is conducted. Dr. Chittawadagi examines areas prone to hernias, like the abdomen and groin. The patient may be instructed to cough or strain, aiding in hernia identification. The examination includes a scrutiny for additional signs such as pain, swelling, or a noticeable bulge in the affected region.
Imaging Tests: When hernia suspicion arises, imaging tests are employed to confirm the diagnosis, including:
Ultrasound: Utilizing high-frequency sound waves, ultrasound generates internal body images. This assists in determining the presence, size, and location of the hernia.
CT Scan: Employing X-rays and advanced computer technology, a CT scan produces detailed internal images. This aids in visualizing the hernia and uncovering any associated underlying conditions.
MRI: Leveraging a potent magnet and radio waves, an MRI creates intricate internal images. This proves beneficial in visualizing the hernia and identifying potential underlying conditions.







